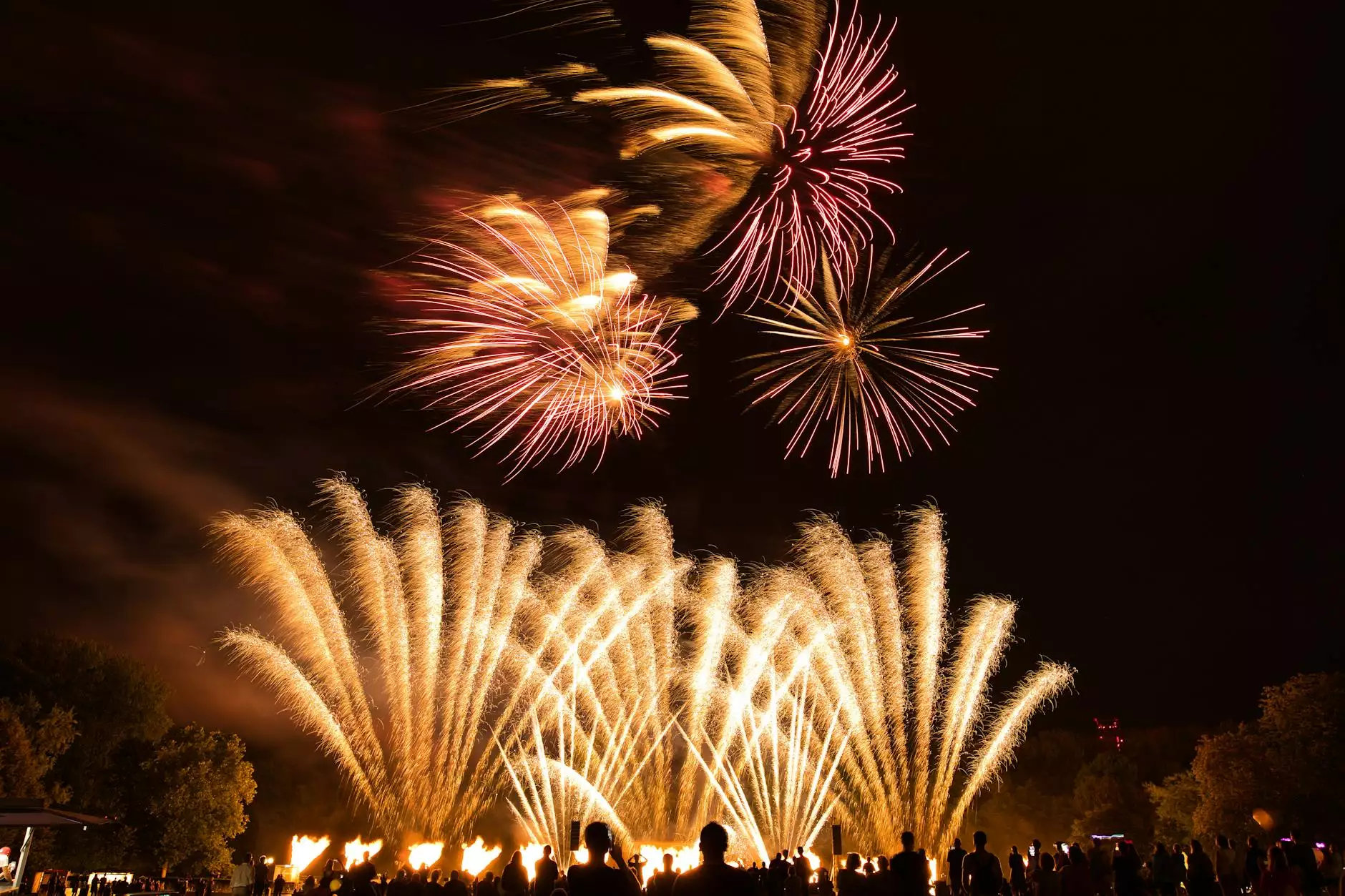
Red, White and Boom! How Fireworks Work

The Science Behind Fireworks
Fireworks have captivated our imaginations for centuries. The stunning displays of light and color that fill the night sky never fail to awe and inspire. But have you ever wondered how fireworks work? Let's delve into the world of pyrotechnics and explore the chemistry behind these magical spectacles.
The Components of a Firework
A typical firework is composed of several key components that work in harmony to create the mesmerizing effects we all love. These components include:
- The Container: This is the outer shell of the firework, typically made of cardboard or plastic. It holds everything together and gives the firework its shape.
- The Fuse: The fuse is the ignition source for the firework. It is usually a thin strip of black powder or a similar material that burns slowly, providing enough time for the firework to be launched into the air.
- The Burst Charge: The burst charge is the heart of the firework. It is a tightly packed mixture of chemicals that explode when ignited, creating the dazzling display of light and color.
- The Pyrotechnic Stars: These are the colorful sparks that we see in the sky. Pyrotechnic stars are small pellets or balls composed of a fuel and an oxidizer. Different combinations of chemicals produce different colors when ignited.
- The Binders: Binders hold the pyrotechnic stars together, ensuring that they burn uniformly. These are usually made of a sticky substance like dextrin or gum arabic.
The Chemistry of Fireworks
Now that we know the basic components of a firework, let's explore the chemistry behind the dazzling display.
Colors in Fireworks
Fireworks create vibrant colors through a process called combustion. Different metal compounds are added to the pyrotechnic stars to generate specific colors. Let's take a closer look at some common colors and the chemicals responsible for them:
- Red: Strontium salts, such as strontium carbonate or strontium nitrate, produce a vibrant red color when ignited.
- White: Titanium or aluminum powders create the brilliant white sparks we see in the sky.
- Blue: Copper compounds, like copper chloride or copper carbonate, are used to achieve a stunning blue hue.
- Green: Barium compounds, such as barium chloride or barium nitrate, create the lush green colors in fireworks.
- Yellow: Sodium compounds, like sodium nitrate or sodium chloride, produce the warm yellow tones in the display.
Creating a Spectacle
Fireworks are carefully choreographed performances, designed to dazzle and amaze the audience. Skilled pyrotechnicians meticulously plan each display, considering factors such as timing, color combinations, and effects.
Various types of fireworks are used to create different visual effects. These include:
- Rockets: Rockets are propelled into the sky using a combination of black powder and a lifting charge. They explode at their peak height, releasing the pyrotechnic stars and creating a burst of color.
- Fountains: Fountains are stationary fireworks that emit showers of sparks and colored flames. They create mesmerizing displays and can be combined to create intricate patterns.
- Sparklers: Sparklers are handheld fireworks that produce a constant stream of sparks. They are often used in celebrations and are popular with children.
- Roman Candles: Roman candles are long tubes filled with pyrotechnic stars. They eject stars one by one, creating a sequence of bursts.
- Catherine Wheels: Catherine wheels are large rotating fireworks that spin and emit sparks in all directions. They create a mesmerizing visual display when mounted on a vertical surface.
Fireworks Safety
While fireworks are undeniably beautiful, it's important to remember that they can be dangerous if mishandled. Here are some safety tips to keep in mind:
- Always follow local laws and regulations: Make sure you understand the laws regarding fireworks in your area and only purchase and use fireworks that comply with the regulations.
- Handle fireworks with care: Never point fireworks at yourself or others. Keep a safe distance and only ignite them in open, outdoor spaces away from flammable materials.
- Supervise children: If children are present, make sure they are supervised by an adult at all times. Sparklers, for example, can reach extremely high temperatures and should only be used under close adult supervision.
- Keep a water source nearby: Have a bucket of water or a hose readily available to extinguish fireworks and to handle any unexpected fires.
Conclusion
Fireworks are more than just beautiful displays of light and color; they are a testament to the power of chemistry and the marvels of human creativity. Understanding the science behind fireworks allows us to appreciate their beauty even more. So the next time you see fireworks lighting up the night sky, you'll have a deeper appreciation for the chemical magic happening above.
At Ward's World, we provide top-notch SEO services in the Business and Consumer Services industry. Our team of experts excels at creating high-quality content, optimizing websites, and boosting search engine rankings. Contact us today to enhance your online presence and drive more traffic to your website.