SolderTip #45: Manual Soldering vs Wave Soldering

Introduction
In the field of business and consumer services, particularly in SEO services, soldering plays a vital role in various industries. Having a thorough understanding of the different soldering techniques available, such as manual soldering and wave soldering, is essential for achieving optimal results. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of both manual soldering and wave soldering, highlighting their differences, advantages, and areas of application.
Manual Soldering
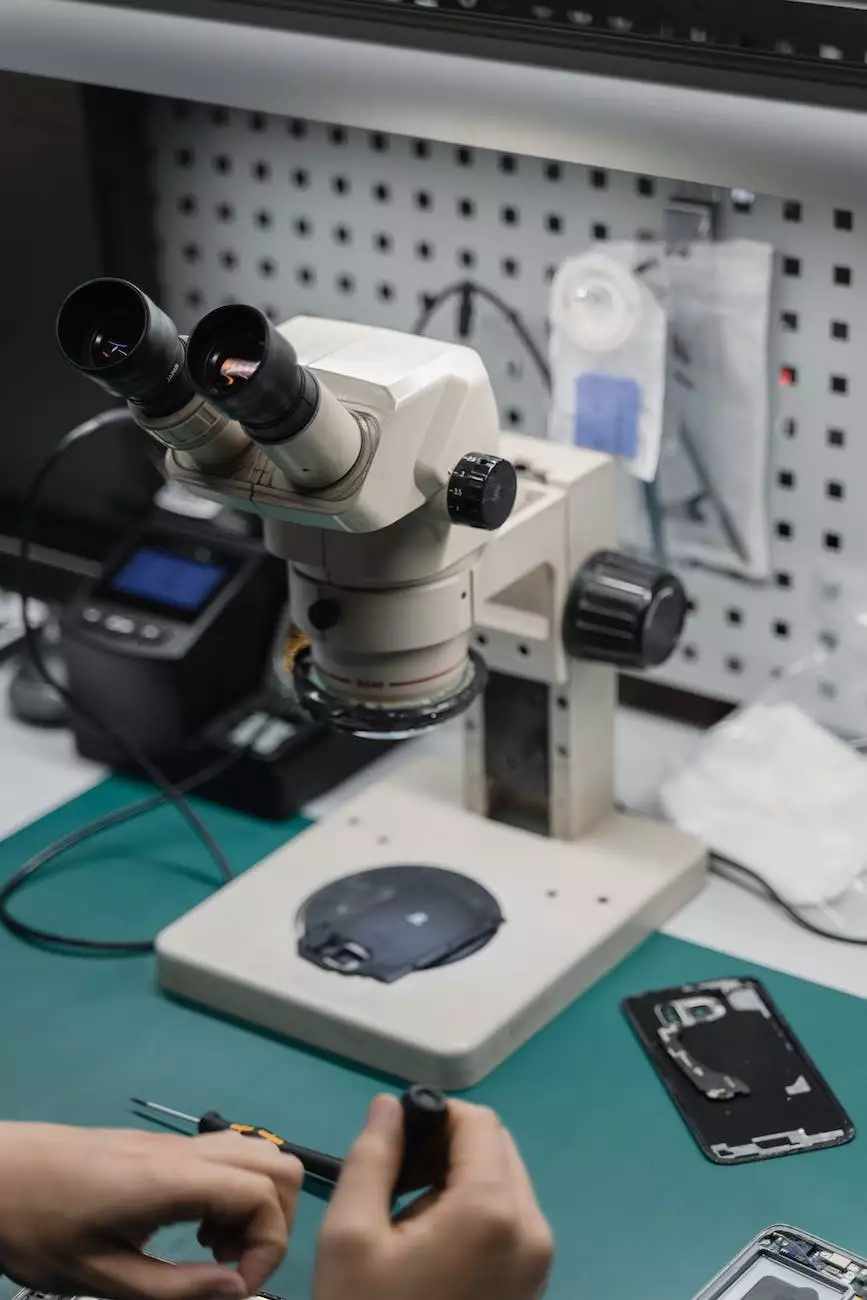
Manual soldering is a technique that involves the use of a soldering iron or soldering gun to join electronic components by melting solder and creating a bond between them. It requires skilled operators who have the necessary experience and precision to carry out the process effectively.
The Process
Manual soldering typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The components to be soldered are prepared, ensuring they are clean and free from contaminants.
- Tinning: The soldering iron tip is coated with solder to aid heat transfer during the soldering process.
- Application: The soldering iron is brought into contact with both the component lead and the pad on the circuit board. The solder is then applied to create a bond.
- Inspection: The soldered joint is visually inspected to ensure it meets quality standards.
Pros and Cons of Manual Soldering
Manual soldering offers several advantages:
- Precision: Skilled operators can achieve precise solder joints, especially in intricate designs.
- Flexibility: Manual soldering allows for greater flexibility in terms of component selection and customization.
- Cost-effective: Manual soldering equipment is usually more affordable compared to wave soldering machines.
However, manual soldering also has its limitations:
- Time-consuming: The manual process can be time-consuming, especially when dealing with large volumes or complex assemblies.
- Operator-dependent: The quality of manual soldering heavily relies on the skills and experience of the operator.
- Higher risk of errors: Human error can lead to soldering defects and potential component damage.
Wave Soldering
Wave soldering is an automated soldering technique commonly used in mass production. It involves passing printed circuit boards (PCBs) over a preheated wave of molten solder, ensuring quick and efficient soldering of multiple connections simultaneously.
The Process
The wave soldering process generally consists of the following steps:
- Flux application: A flux is applied to the PCBs to remove any oxides and to promote better solder wetting.
- Preheating: The PCBs are preheated to a specific temperature to help prepare the surfaces for soldering.
- Wave soldering: The PCBs are conveyed over a wave of molten solder, which facilitates the soldering of the components.
- Cooling and cleaning: The soldered PCBs are cooled and then undergo a cleaning process to remove any flux residues.
- Inspection: The solder joints are inspected to ensure their quality and reliability.
Pros and Cons of Wave Soldering
Wave soldering offers several advantages:
- Time-efficient: Wave soldering allows for quick and simultaneous soldering of multiple connections, making it ideal for mass production.
- Consistent results: The automated process ensures consistent solder quality and reduces the risk of human error.
- Lower labor costs: Wave soldering requires minimal manual intervention, resulting in reduced labor costs.
However, wave soldering also has its limitations:
- Less customization: Wave soldering may not be suitable for complex assemblies that require component customization.
- Costly setup: Wave soldering machines can be expensive to set up, making it less viable for small-scale operations.
- Greater material usage: Wave soldering typically requires more solder compared to manual soldering, leading to higher material costs.
Conclusion
Both manual soldering and wave soldering have their own merits in the field of business and consumer services, specifically in SEO services. The choice between the two techniques depends on various factors, such as the volume of production, complexity of the circuit design, level of customization required, and available budget. Understanding the differences, advantages, and limitations of manual soldering and wave soldering enables businesses to make informed decisions to achieve optimal soldering outcomes.